SQL Server can serve as a central hub for accessing and integrating data from various sources. Here are some ideas:
1. Linked Servers
- Connect to other SQL Server instances, Oracle, MySQL, or other databases.
- Use
sp_addlinkedserverto configure connections. - Query remote data with
OPENQUERYor four-part naming. -
For instance, Active Directory can be linked server
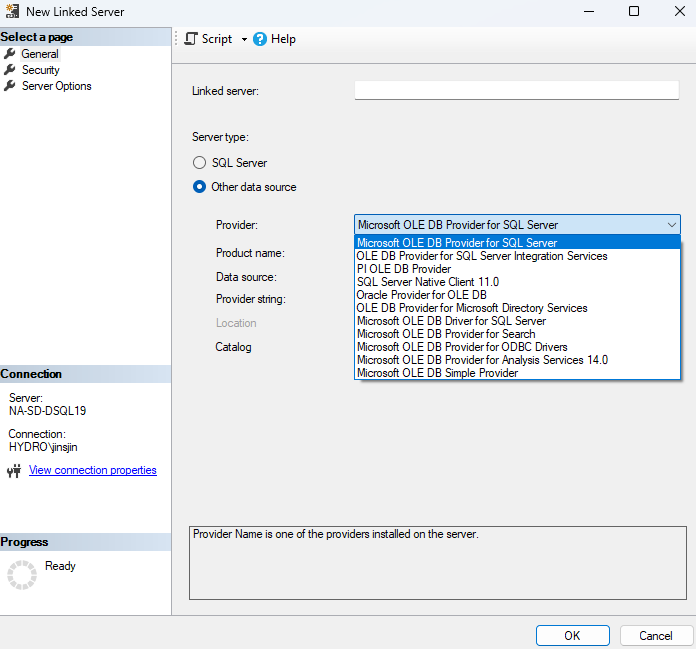
-
Example code querying AD (ADSI below is the linked server name)
SELECT sAMAccountName,
name,
mail,
title,
employeeID,
displayName,
employeeType
userPrincipalName
FROM OPENQUERY(ADSI, 'SELECT sAMAccountName,
name,
mail,
department,
company,
title,
telephoneNumber,
userAccountControl,
manager,
distinguishedName,
employeeID,
displayName,
employeeType,
userPrincipalName
FROM ''LDAP://DC=hydro,DC=local''
WHERE objectCategory=''user''')
2. External Data Sources (PolyBase)
- Integrate data from Hadoop, Azure Blob Storage, or other external sources.
-
Use PolyBase to query external tables as if they were local.
-
check one example to access Azure Blob Storage here
3. Calling APIs from SQL Server
- Use CLR integration to write .NET code for HTTP requests.
-
Use SQL Server Agent jobs or external scripts (e.g., PowerShell) to fetch API data and load into tables.
-
check it here
4. Data Virtualization
- Create views that combine data from multiple sources.
- Use synonyms for easier access to remote objects.
5. Import/Export Data
- Use SSIS (SQL Server Integration Services) for ETL processes.
- Automate data movement between SQL Server and other systems.
6. Security and Auditing
- Centralize access control and auditing for all connected data sources.
7. Real-Time Data Integration
- Use Change Data Capture (CDC) or Change Tracking to sync data across systems.
Tip: Always consider performance, security, and data consistency when integrating external sources.